
The Energy Innovation Test Station at the University of Szeged, a unique facility in Central Europe, has been built and is starting its operation! Inauguration ceremony: May 16th, 2024.
The laboratory-scale expertise acquired by our researchers at the University of Szeged (Szegedi Tudományegyetem, SZTE) will be utilized in a semi-industrial environment at the Energy Innovation Test Station (EIT), a system integrating multiple technologies.
Defining our goals
The aim of the EIT is 1) to demonstrate experiments and technologies for industrial partners at an industrially relevant scale; 2) to showcase the operation of various energy technologies and to facilitate their deployment; 3) to enable direct and well-founded comparison of the integration methods of energy technologies and different components; 4) to test new catalysts and reactors; 5) to make the site serve as a large laboratory that is also capable of adopting and servicing additional technological containers.
50 kW solar power plant
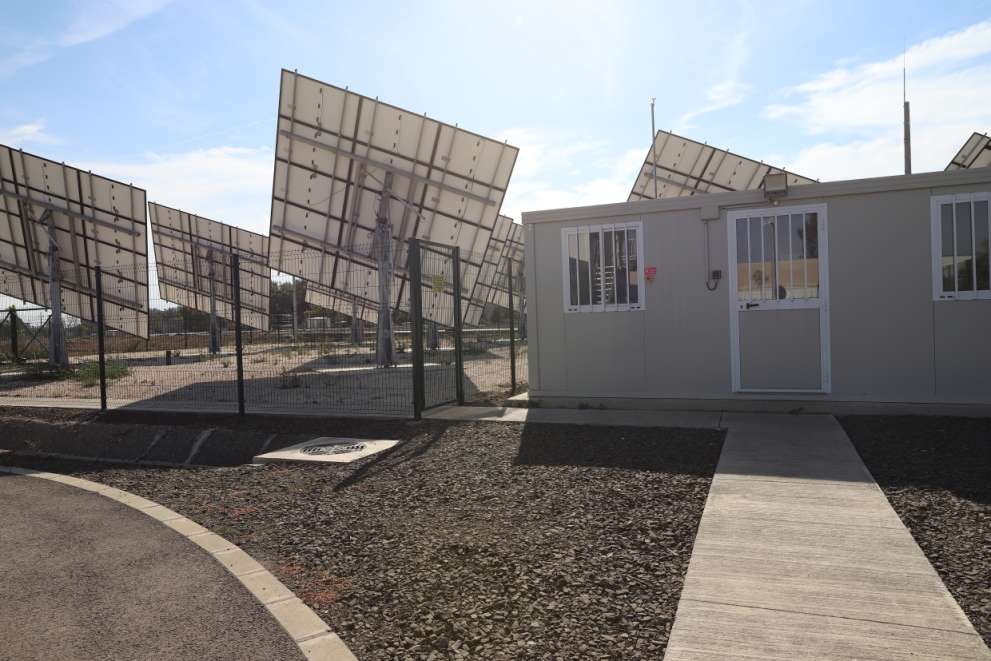
As the first step in the implementation of the EIT, a 50 kW photovoltaic power plant (solar farm) was built in the SZTE Science Park in 2023. In addition to the conventional grid supply, electrolysis can thus be implemented in a “green” way at the EIT, using electricity from the solar farm. This setup also allows for the simulation of EIT technologies' “island-mode” operation, hence investigating the effect of the dynamically changing reaction conditions.
The Power-to-Gas (PtG) container
The EIT site, including the containerized PtG technologies and the control systems, was designed by researchers from the University of Szeged in collaboration with a Hungarian engineering office, and the whole system was assembled by a Hungarian contractor. The two PtG technologies are the following:
PEM water electrolysis: E-hydrogen can be produced by water electrolysis. This hydrogen will be utilized as a fuel, or as feedstock in further energy conversion processes. Key parameters:
- Only the electrolyzer stack is from a commercial source
- Maximum H2 production rate: 10 Nm3/h
- Maximum electrolysis input power: 50 kW
- H2 storage pressure: 40 bar

CO2 electrolysis technology: Technology aimed at the electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide. Key parameters:
- Direct electrochemical conversion of CO2 into industrial feedstock
- CO2 conversion into gaseous products (CO, CH4, C2H4)
- Maximum CO2 feed rate: 300 Nl/min
- CO production up to 10 bar pressure

The Gas-to-Liquid (GtL) container
The GtL technology is suitable for the catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide into synthetic fuels through their thermocatalystic reactions with hydrogen. The five-reactor test system utilizes electrochemically produced CO and H₂, enabling the three technologies to convert CO₂ and e-hydrogen into liquid fuels, using energy generated by the solar power plant. The GtL technology can facilitate both the direct hydrogenation of carbon dioxide and a two-step process via CO, producing liquid e-fuels. The resulting synthetic crude fuel resembles naturally extracted crude oil, from which gasoline, diesel, kerosene, and even heavier oils or waxes can be derived. EIT researchers collaborate closely with Hungarian and international industry leaders (e.g., MOL, Audi) on the processing and utilization of e-fuels. For instance, Audi Hungaria plans to test the produced e-fuel in its engines by mixing it with conventional gasoline, assessing both its short- and long-term effects.
The EIT represents an intermediate scale between large laboratories and pilot plants: production occurring in kilogram-per-day quantities. This is a 1,000-fold increase compared to laboratory-scale operations.
What can be tested, examined at the EIT?
- a wide range of energy conversion and storage processes
- system components (e.g. pressure regulators), subsystems (e.g. water purifiers)
- catalysts, reactors
- cell stacks, complete containers
- production processes based on various industrial gases (e.g. carbon dioxide)
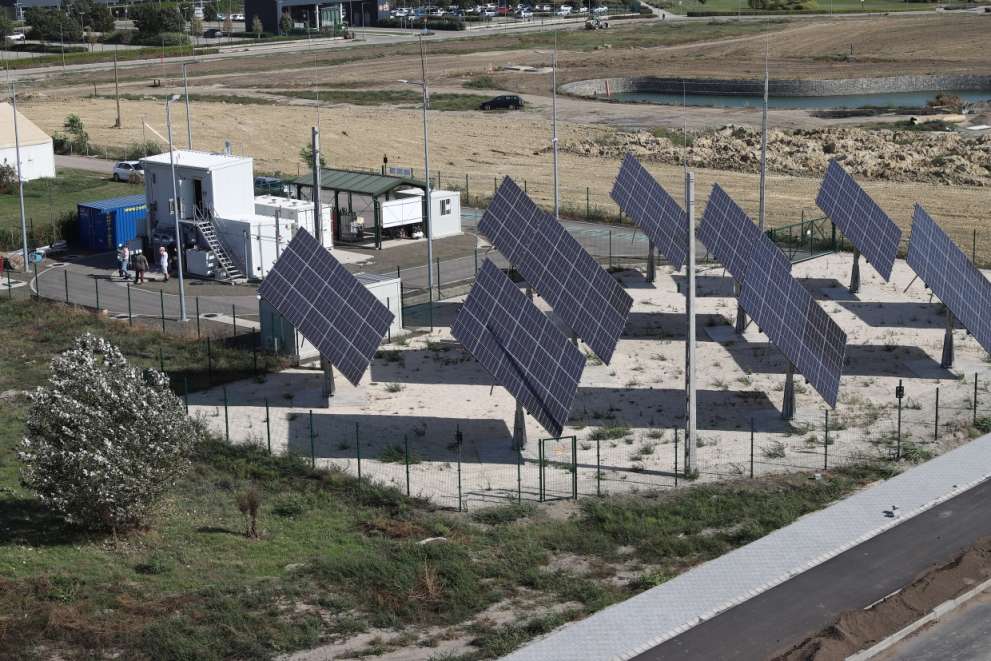






The test station was implemented with the financing from the "Development of an innovative energy storage technology utilizing renewable electricity from the Bükkábrány solar power plant", the "National Laboratory for Renewable Energy" and the "Development and validation of synthetic fuels in a corporate environment" projects.


Summary of the Inauguration Ceremony of the University of Szeged Energy Innovation Test Station
Szeged, May 16, 2024
